PRIVATE USE VS. PUBLIC USE
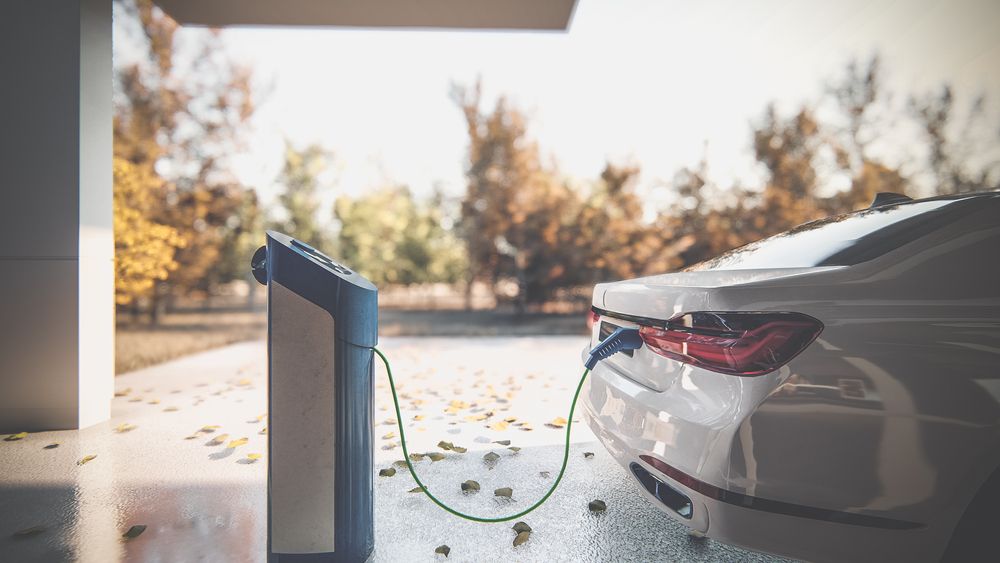
Home and offices are the most common places to recharge batteries for most EV drivers. While they are convenient and allow for long(er) charging sessions, they aren’t the most effective setups. Here’s why.
The technical explanation
Charging speed isn’t only reliant on the charging station. It also depends on the electric capacity of the infrastructure it’s attached to.
As an example, most private EV charging stations can deliver from 11 to 22 kW (assuming the presence of a main fuse with a rating of 3 x 32 A, or amps, for the latter). That said, it is still very common to see 1.7kW / 1 x 8 A and 3.7kW / 1x 16A chargers installed.
It’s important to note that the electrical supply will always be measured in amps (amperage) and not in voltage. The higher the amps, the more electrical load a building can handle.
Considering that there are essentially 4 charging speeds, 22 kW falls in the lower tier:
Slow charging (AC, 3-7 kW)
Medium charging (AC, 11-22 kW)
Fast charging (AC, 43 kW and (CCS, 50 kW)
Ultra fast charging (CCS, >100 kW)
What’s more, many residential buildings currently have main fuses smaller than 32 A, so it’s essential to keep this in mind when estimating at-home charging speeds and charging times.
It’s certainly possible to upgrade a residence’s charging capabilities, but this will require the help of a skilled electrician and is not exactly cost-effective. Fortunately, it’s possible to account for amp limitations by restricting the maximum power of a charging device using the Virta admin panel. This kind of control over your EV charging points is essential to prevent dangers such as over-charging, under-charging, circuit damage, or even fire.
Electric Car 32A Home Wall Mounted Ev Charging Station 7KW EV Charger
Post time: Nov-14-2023