Level 1 vs. Level 2 vs. Level 3 charging stations: What’s the difference?

You’re probably familiar with octane ratings (regular, mid-grade, premium) at gas stations. Electric vehicle charger levels are similar, but instead of measuring the quality of fuel, EV levels denote the power output of a charging station. The higher the electrical output, the faster an EV will charge. Let’s compare Level 1 vs. Level 2 vs. Level 3 charging stations.
Level 1 charging stations
Level 1 charging consists of a nozzle cord plugged into a standard 120V electrical outlet. EV drivers get a nozzle cord, called the emergency charger cable or the portable charger cable, with their purchase of an EV. This cable is compatible with the same type of outlet in your house used to charge a laptop or phone.
The majority of passenger EVs have a built-in SAE J1772 charge port, also known as the J plug, which allows them to use standard electrical outlets for Level 1 charging or Level 2 charging stations. Tesla owners have a different charging port but can purchase a J-plug adapter if they want to plug it into an outlet at home or use a non-Tesla Level 2 charger.
Level 1 charging is affordable and requires no special setup or additional hardware or software, making it a convenient choice for residential use. However, it may take up to 24 hours to fully charge a battery, which makes Level 1 charging impractical for drivers that log a lot of miles on a daily basis.
For an in-depth look at Level 1 charging stations, read What is a Level 1 charger for electric vehicles? next.
Level 2 charging stations
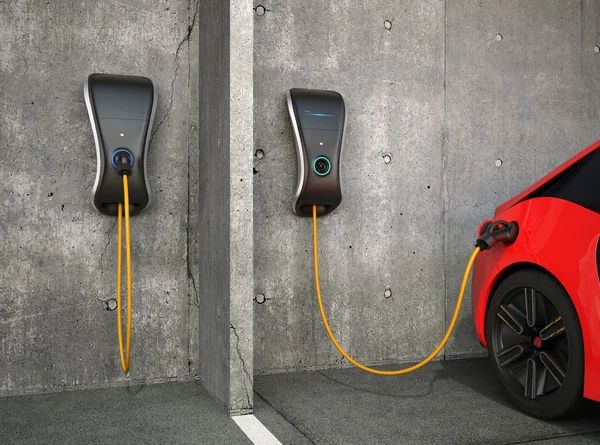
Level 2 charging stations use 240V electric outlets, which means they can charge an EV much faster than Level 1 chargers due to higher energy output. An EV driver can connect to a Level 2 charger with the attached nozzle cord using the integrated J plug built into most EVs.
Level 2 chargers are often equipped with software that can intelligently charge an EV, adjust power levels, and bill the customer appropriately. That fact is reflected in the cost, making Level 2 chargers a larger investment. However, they’re an ideal option for apartment complexes, retail spaces, employers, and university campuses that want to offer EV charging stations as a perk.
There are many Level 2 charger options on the market, so resellers and network owners who want maximum flexibility may want to consider hardware-agnostic EV charging station management software that works with any OCPP-compliant charger and allows them to manage their devices from one central hub.
Check out What is a Level 2 charger for electric vehicles? to learn more about Level 2 charging.
Level 3 charging stations
A Level 3 charger is the hostess with the mostest in the world of EV charging, because it uses direct current (DC) to charge EVs much faster than both Level 1 and Level 2 chargers. Level 3 chargers are often called DC chargers or “superchargers” due to their ability to fully charge an EV in under an hour.
However, they’re not as standardized as lower-level chargers, and an EV requires special components like a Combined Charging System (CCS or “Combo”) plug or a CHAdeMO plug used by some Asian automotive manufacturers, to connect to a Level 3 charger.
You’ll find Level 3 chargers alongside main thoroughfares and highways because while most passenger EVs can use them, DC chargers are primarily designed for commercial and heavy-duty EVs. A fleet or a network operator can mix and match a selection of Level 2 and Level 3 chargers on-site if they’re using compatible open software.
7kw Single Phase Type1 Level 1 5m Portable AC Ev Charger For Car America
Post time: Oct-31-2023