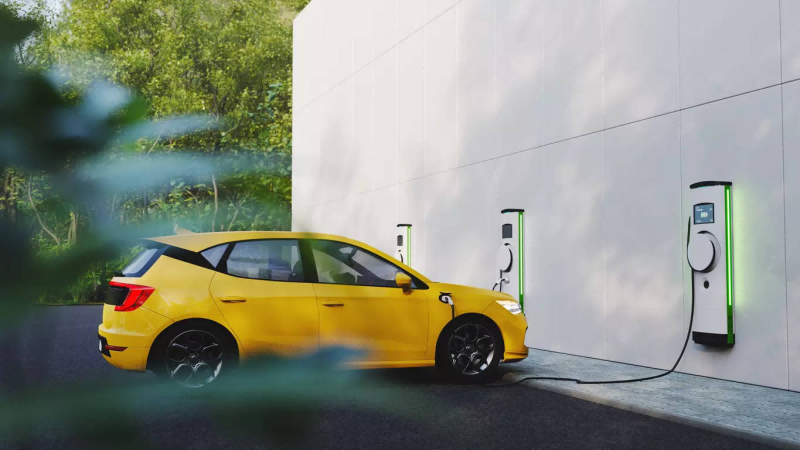
As the popularity of electric vehicles continues to grow, the demand for electric vehicle (EV) chargers has increased significantly. The two main types of EV chargers available today are alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) chargers. While both types of EV battery charge the same purpose, it’s important to understand the differences between the two.
AC EV chargers, also known as Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, are the most common type of charger used in residential and public locations. AC chargers use the same type of electricity that powers homes and businesses, so they’re easy to install and use. Level 1 chargers typically require a standard 120V outlet and can provide a range of 4 miles per hour. Level 2 chargers, on the other hand, require a dedicated 240V outlet and can provide up to 25 miles of range per hour. These chargers are often used in public parking lots, workplaces and other places where faster charging is required.
DC chargers, also known as Level 3 chargers or fast chargers, are more powerful than AC chargers and are primarily used on highways, in commercial locations and where EV drivers need fast charging. DC chargers use a different type of electricity and require more complex equipment to provide up to 250 miles of charging range in as little as 30 minutes. While AC chargers can be used with any EV, DC chargers require a vehicle with a specific type of port and are usually found on newer EV models.
The main difference between AC and DC chargers is the charging speed and the equipment required to use them. AC chargers are the most common type of charger and can be used almost anywhere, while DC chargers offer faster charging but require specific vehicle compatibility and are less common. AC chargers are great for everyday use and long-term charging, while DC chargers are mainly used for emergency charging or long trips that require a quick charge.
In addition to differences in speed and equipment, there are also differences in cost and availability. AC chargers are generally cheaper and easier to install, while DC chargers are more expensive and require more complex electrical infrastructure. While AC chargers are ubiquitous, DC chargers are still relatively uncommon, usually located on highways or in commercial areas.
When choosing an AC or DC EV charger, it’s important to consider your daily driving habits and charging needs. If you primarily use your EV for short commutes and have easy access to a Level 1 or 2 charger, then you probably only need an AC charger. However, if you often travel long distances and need fast charging, a DC charger may be the best option for you.
In conclusion, both AC and DC EV chargers have their unique advantages and disadvantages. AC chargers are more common, cheaper and easier to use, while DC chargers offer faster charging but require specific vehicle compatibility and more complex infrastructure. As the demand for EV chargers continues to grow, it is important to understand the differences between the two chargers and choose the one that best suits your needs.
Post time: May-09-2023