As of my last knowledge update in September 2021, the home electric vehicle (EV) charging industry was already undergoing significant advancements and changes. However, I do not have information on developments beyond that date. Up until 2021, several trends and technologies were shaping the new era of home EV chargers:
Faster Charging Speeds: Home EV chargers were becoming increasingly powerful, offering faster charging speeds to reduce charging times. This was made possible by advancements in charging technology and higher power delivery capabilities.
Smart Charging: Many home EV chargers were incorporating smart features, allowing users to schedule charging times, monitor charging progress remotely through smartphone apps, and even integrate with smart home systems. This helped users take advantage of off-peak electricity rates and optimize charging based on their daily routines.
Integration with Renewable Energy: Some home EV charging solutions were being designed to integrate with residential solar panels and other renewable energy sources. This allowed EV owners to charge their vehicles using clean and sustainable energy, further reducing their carbon footprint.
Load Management and Grid Integration: Home EV chargers were being developed with load management capabilities to prevent overloading the electrical grid. This was particularly important as more EVs were being adopted, ensuring that charging demand was distributed efficiently.
Wireless Charging: Wireless charging technology for EVs was also under development for home use. This technology eliminates the need for physical cables and connectors, making charging more convenient and reducing wear and tear on components.
Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) and Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Integration: Some home EV chargers were exploring the concept of V2H and V2G integration. V2H allows EVs to supply power back to the home in case of power outages, acting as a temporary backup power source. V2G technology enables EVs to discharge excess energy back to the grid during peak demand, potentially providing a source of revenue for EV owners.
Modular and Scalable Designs: Home EV chargers were being designed with modular and scalable features, allowing homeowners to expand their charging infrastructure as their EV fleet grew or as their charging needs evolved.
User-Friendly Designs: User experience was a focus, with many home EV chargers featuring intuitive interfaces, easy installation processes, and compatibility with a wide range of EV makes and models.
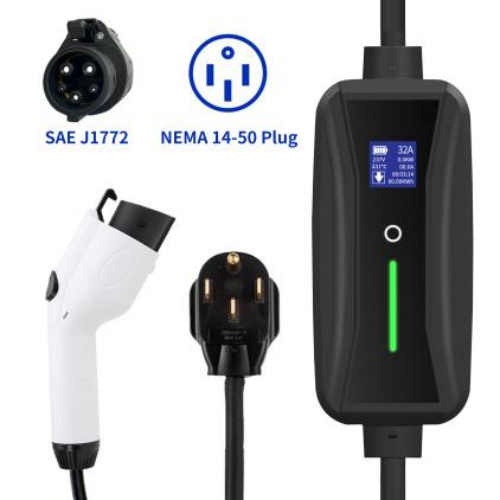
32A Electric Vehicle Level 2 Mode2 Cable EV Portable Charger with Type 1 plug and NEMA 14-50
Post time: Aug-17-2023